ChatGPT is great at answering questions and generating code. But here’s what it can’t do: execute that code, query your actual database, create a GitHub repo with your project, or scrape live data from websites. It’s like having a brilliant advisor who can only talk, never act.
Docker MCP Toolkit changes this completely.
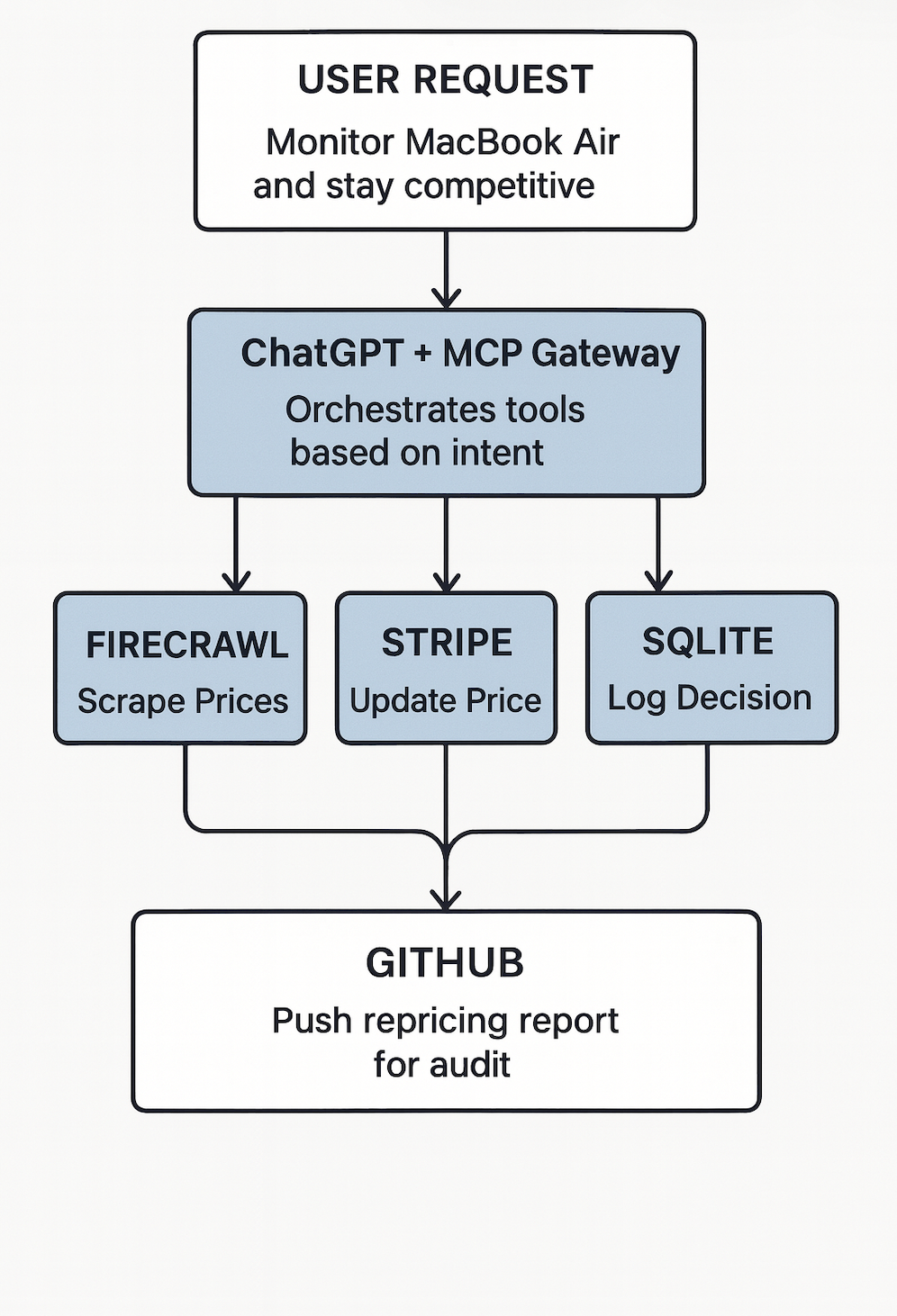
Here’s what that looks like in practice: You ask ChatGPT to check MacBook Air prices across Amazon, Walmart, and Best Buy. If competitor prices are lower than yours, it doesn’t just tell you, it acts: automatically adjusting your Stripe product price to stay competitive, logging the repricing decision to SQLite, and pushing the audit trail to GitHub. All through natural conversation. No manual coding. No copy-pasting scripts. Real execution.
“But wait,” you might say, “ChatGPT already has a shopping research feature.” True. But ChatGPT’s native shopping can only lookup prices. Only MCP can execute: creating payment links, generating invoices, storing data in your database, and pushing to your GitHub. That’s the difference between an advisor and an actor.
By the end of this guide, you’ll build exactly this: a Competitive Repricing Agent that checks competitor prices on demand, compares them to yours, and automatically adjusts your Stripe product prices when competitors are undercutting you.
Here’s how the pieces fit together:
- ChatGPT provides the intelligence: understanding your requests and determining what needs to happen
- Docker MCP Gateway acts as the secure bridge: routing requests to the right tools
- MCP Servers are the hands: executing actual tasks in isolated Docker containers
The result? ChatGPT can query your SQL database, manage GitHub repositories, scrape websites, process payments, run tests, and more—all while Docker’s security model keeps everything contained and safe.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to add seven MCP servers to ChatGPT by connecting to Docker MCP Toolkit. We’ll use a handful of must-have MCP servers: Firecrawl for web scraping, SQLite for data persistence, GitHub for version control, Stripe for payment processing, Node.js Sandbox for calculations, Sequential Thinking for complex reasoning, and Context7 for documentation. Then, you’ll build the Competitive Repricing Agent shown above, all through conversation.
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
Before we dive into the setup, let’s clarify what MCP actually is.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is the standardized way AI agents like ChatGPT and Claude connect to tools, APIs, and services. It’s what lets ChatGPT go beyond conversation and perform real-world actions like querying databases, deploying containers, analyzing datasets, or managing GitHub repositories.
In short: MCP is the bridge between ChatGPT’s reasoning and your developer stack. And Docker? Docker provides the guardrails that make it safe.
Why Use Docker MCP Toolkit with ChatGPT?
I’ve been working with AI tools for a while now, and this Docker MCP integration stands out for one reason: it actually makes ChatGPT productive.
Most AI integrations feel like toys: impressive demos that break in production. Docker MCP Toolkit is different. It creates a secure, containerized environment where ChatGPT can execute real tasks without touching your local machine or production systems.
Every action happens in an isolated container. Every MCP server runs in its own security boundary. When you’re done, containers are destroyed. No residue, no security debt, complete reproducibility across your entire team.
What ChatGPT Can and Can’t Do Without MCP
Let’s be clear about what changes when you add MCP.
Without MCP
You ask ChatGPT to build a system to regularly scrape product prices and store them in a database. ChatGPT responds with Python code, maybe 50 lines using BeautifulSoup and SQLite. Then you must copy the code, install dependencies, create the database schema, run the script manually, and set up a scheduler if you want it to run regularly.
Yes, ChatGPT remembers your conversation and can store memories about you. But those memories live on OpenAI’s servers—not in a database you control.
With MCP
You ask ChatGPT the same thing. Within seconds, it calls Firecrawl MCP to actually scrape the website. It calls SQLite MCP to create a database on your machine and store the data. It calls GitHub MCP to save a report to your repository. The entire workflow executes in under a minute.
Real data gets stored in a real database on your infrastructure. Real commits appear in your GitHub repository. Close ChatGPT, come back tomorrow, and ask “Show me the price trends.” ChatGPT queries your SQLite database and returns results instantly because the data lives in a database you own and control, not in ChatGPT’s conversation memory.
The data persists in your systems, ready to query anytime; no manual script execution required.
Why This Is Different from ChatGPT’s Native Shopping
ChatGPT recently released a shopping research feature that can track prices and make recommendations. Here’s what it can and cannot do:
What ChatGPT Shopping Research can do:
- Track prices across retailers
- Remember price history in conversation memory
- Provide comparisons and recommendations
What ChatGPT Shopping Research cannot do:
- Automatically update your product prices in Stripe
- Execute repricing logic based on competitor changes
- Store pricing data in your database (not OpenAI’s servers)
- Push audit trails to your GitHub repository
- Create automated competitive response workflows
With Docker MCP Toolkit, ChatGPT becomes a competitive pricing execution system. When you ask it to check prices and competitors are undercutting you, it doesn’t just inform you, it acts: updating your Stripe prices to match or beat competitors, logging decisions to your database, and pushing audit records to GitHub. The data lives in your infrastructure, not OpenAI’s servers.
Setting Up ChatGPT with Docker MCP Toolkit
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- A machine with 8 GB RAM minimal, ideally 16GB
- Install Docker Desktop
- A ChatGPT Plus, Pro, Business, or Enterprise Account
- ngrok account (free tier works) – For exposing the Gateway publicly
Step 1. Enable ChatGPT developer mode
- Head over to ChatGPT and create a new account.
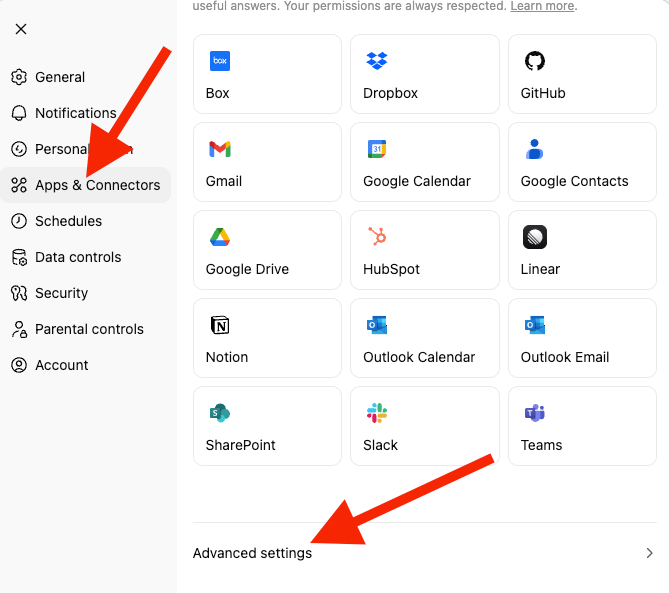
- Click on your profile icon at the top left corner of the ChatGPT page and select “Settings”. Select “Apps and Connectors” and scroll down to the end of the page to select “Advanced Settings.”
Settings → Apps & Connectors → Advanced → Developer Mode (ON)
ChatGPT Developer Mode provides full Model Context Protocol (MCP) client support for all tools, both read and write operations. This feature was announced in the first week of September 2025, marking a significant milestone in AI-developer integration. ChatGPT can perform write actions—creating repositories, updating databases, modifying files—all with proper confirmation modals for safety.
Key capabilities:
- Full read/write MCP tool support
- Custom connector creation
- OAuth and authentication support
- Explicit confirmations for write operations
- Available on Plus, Pro, Business, Enterprise, and Edu plans
Step 2. Create MCP Gateway
This creates and starts the MCP Gateway container that ChatGPT will connect to.
docker mcp server init --template=chatgpt-app-basic test-chatgpt-app
Successfully initialized MCP server project in test-chatgpt-app (template: chatgpt-app-basic)
Next steps:
cd test-chatgpt-app
docker build -t test-chatgpt-app:latest .
Step 3. List out all the project files
ls -la
total 64
drwxr-xr-x@ 9 ajeetsraina staff 288 16 Nov 16:53 .
drwxr-x---+ 311 ajeetsraina staff 9952 16 Nov 16:54 ..
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 165 16 Nov 16:53 catalog.yaml
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 371 16 Nov 16:53 compose.yaml
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 480 16 Nov 16:53 Dockerfile
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 88 16 Nov 16:53 go.mod
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 2576 16 Nov 16:53 main.go
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 2254 16 Nov 16:53 README.md
-rw-r--r--@ 1 ajeetsraina staff 6234 16 Nov 16:53 ui.html
Step 4. Examine the Compose file
services:
gateway:
image: docker/mcp-gateway # Official Docker MCP Gateway image
command:
- --servers=test-chatgpt-app # Name of the MCP server to expose
- --catalog=/mcp/catalog.yaml # Path to server catalog configuration
- --transport=streaming # Use streaming transport for real-time responses
- --port=8811 # Port the gateway listens on
environment:
- DOCKER_MCP_IN_CONTAINER=1 # Tells gateway it's running inside a container
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock # Allows gateway to spawn sibling containers
- ./catalog.yaml:/mcp/catalog.yaml # Mount local catalog into container
ports:
- "8811:8811" # Expose gateway port to host
Step 5. Bringing up the compose services
docker compose up -d
[+] Running 2/2
✔ Network test-chatgpt-app_default Created 0.0s
✔ Container test-chatgpt-app-gateway-1 Started
docker ps | grep test-chatgpt-app
eb22b958e09c docker/mcp-gateway "/docker-mcp gateway…" 21 seconds ago Up 20 seconds 0.0.0.0:8811->8811/tcp, [::]:8811->8811/tcp test-chatgpt-app-gateway-1
Step 6. Verify the MCP session
curl http://localhost:8811/mcp
GET requires an active session
Step 7. Expose with Ngrok
Install ngrok and expose your local gateway. You will need to sign up for an ngrok account to obtain an auth token.
brew install ngrok
ngrok config add-authtoken <your_token_id>
ngrok http 8811
Note the public URL (like https://91288b24dc98.ngrok-free.app). Keep this terminal open.
Step 8. Connect ChatGPT
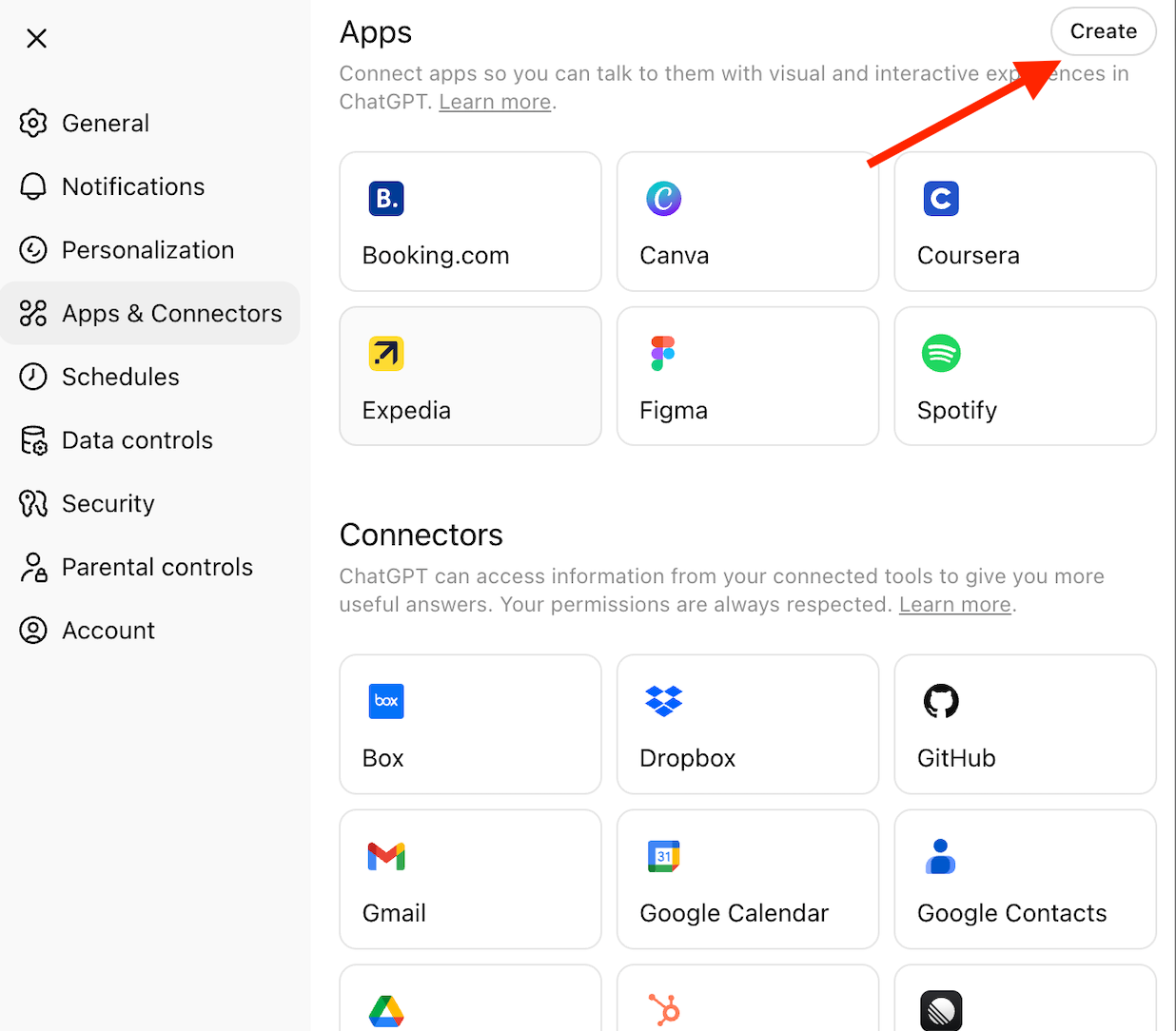
In ChatGPT, go to Settings → Apps & Connectors → Create.
Step 9. Create connector:
Settings → Apps & Connectors → Create
- Name: Test MCP Server
- Description: Testing Docker MCP Toolkit integration
- Connector URL: https://[YOUR_NGROK_URL]/mcp
- Authentication: None
- Click "Create"
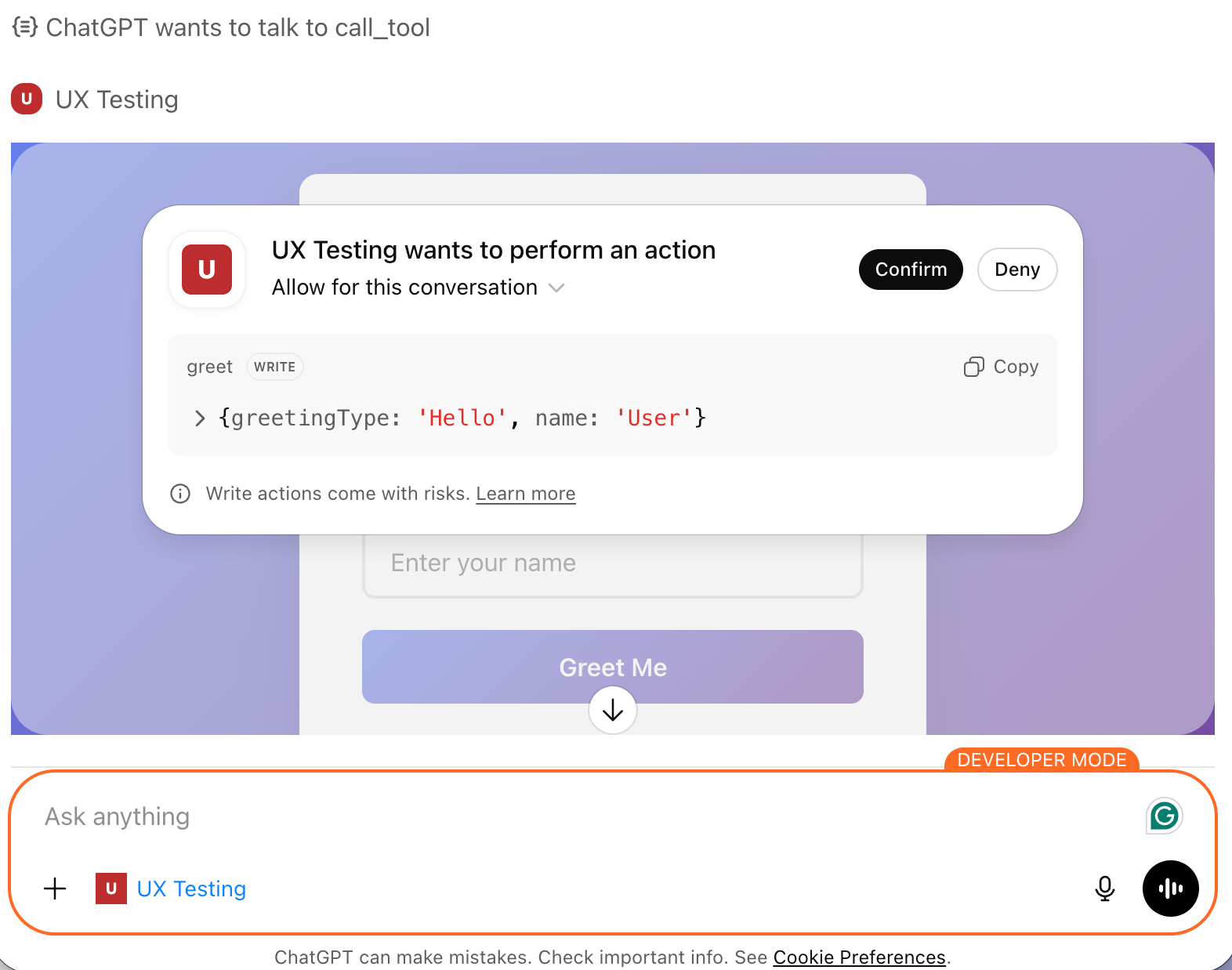
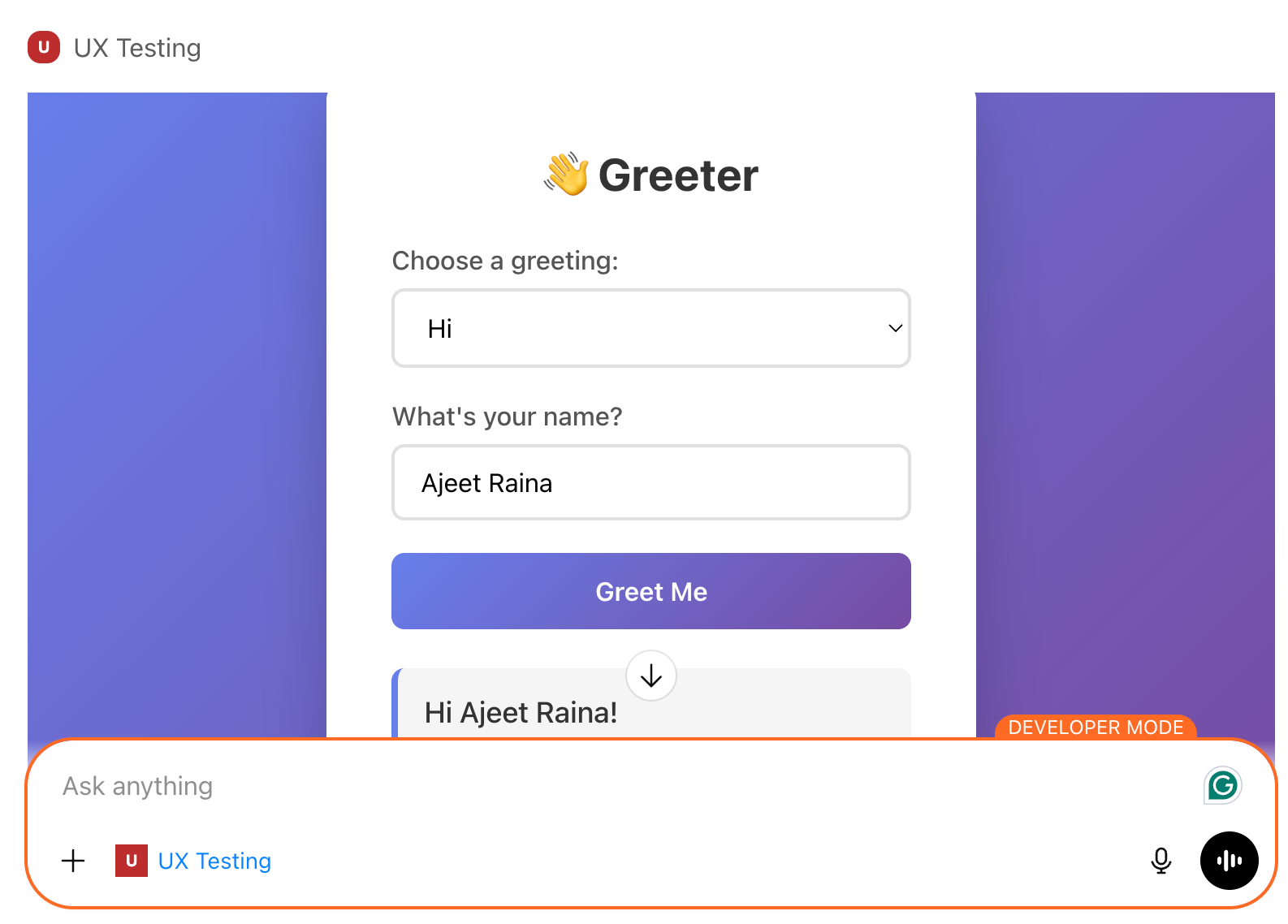
Test it by asking ChatGPT to call the greet tool. If it responds, your connection works. Here’s how it looks:
Real-World Demo: Competitive Repricing Agent
Now that you’ve connected ChatGPT to Docker MCP Toolkit, let’s build something that showcases what only MCP can do—something ChatGPT’s native shopping feature cannot replicate.
We’ll create a Competitive Repricing Agent that checks competitor prices on demand, and when competitors are undercutting you, automatically adjusts your Stripe product prices to stay competitive, logs the repricing decision to SQLite, and pushes audit records to GitHub.
Time to build: 15 minutes
Monthly cost: Free Stripe (test mode) + $1.50-$15 (Firecrawl API)
Infrastructure: $0 (SQLite is free)
The Challenge
E-commerce businesses face a constant dilemma:
- Manual price checking across multiple retailers is time-consuming and error-prone
- Comparing competitor prices and calculating optimal repricing requires multiple tools
- Executing price changes across your payment infrastructure requires context-switching
- Historical trend data is scattered across spreadsheets
- Strategic insights require manual analysis and interpretation
Result: Missed opportunities, delayed reactions, and losing sales to competitors with better prices.
The Solution: On-Demand Competitive Repricing Agent
Docker MCP Toolkit transforms ChatGPT from an advisor into an autonomous agent that can actually execute. The architecture routes your requests through a secure MCP Gateway that orchestrates specialized tools: Firecrawl scrapes live prices, Stripe creates payment links and invoices, SQLite stores data on your infrastructure, and GitHub maintains your audit trail. Each tool runs in an isolated Docker container: secure, reproducible, and under your control.
The 7 MCP Servers We’ll Use
|
Firecrawl
|
Web scraping
|
Extracts live prices from any website
|
|
SQLite
|
Data persistence
|
Stores 30+ days of price history
|
|
Stripe
|
Payment management
|
Updates your product prices to match or beat competitors
|
|
GitHub
|
Version control
|
Audit trail for all reports
|
|
Sequential Thinking
|
Complex reasoning
|
Multi-step strategic analysis
|
|
Context7
|
Documentation
|
Up-to-date library docs for code generation
|
|
Node.js Sandbox
|
Calculations
|
Statistical analysis in isolated containers
|
The Complete MCP Workflow (Executes in under 3 minutes)
Step 1. Scrape and Store (30 seconds)
- Agent scrapes live prices from Amazon, Walmart, and Best Buy
- Compares against your current Stripe product price
Step 2: Compare Against Your Price (15 seconds)
- Best Buy drops to $509.99—undercutting your $549.99
- Agent calculates optimal repricing strategy
- Determines new competitive price point
Step 3: Execute Repricing (30 seconds)
- Updates your Stripe product with the new competitive price
- Logs repricing decision to SQLite with full audit trail
- Pushes pricing change report to GitHub
Step 4: Stay Competitive (instant)
- Your product now priced competitively
- Complete audit trail in your systems
- Historical data ready for trend analysis
The Demo Setup: Enable Docker MCP Toolkit
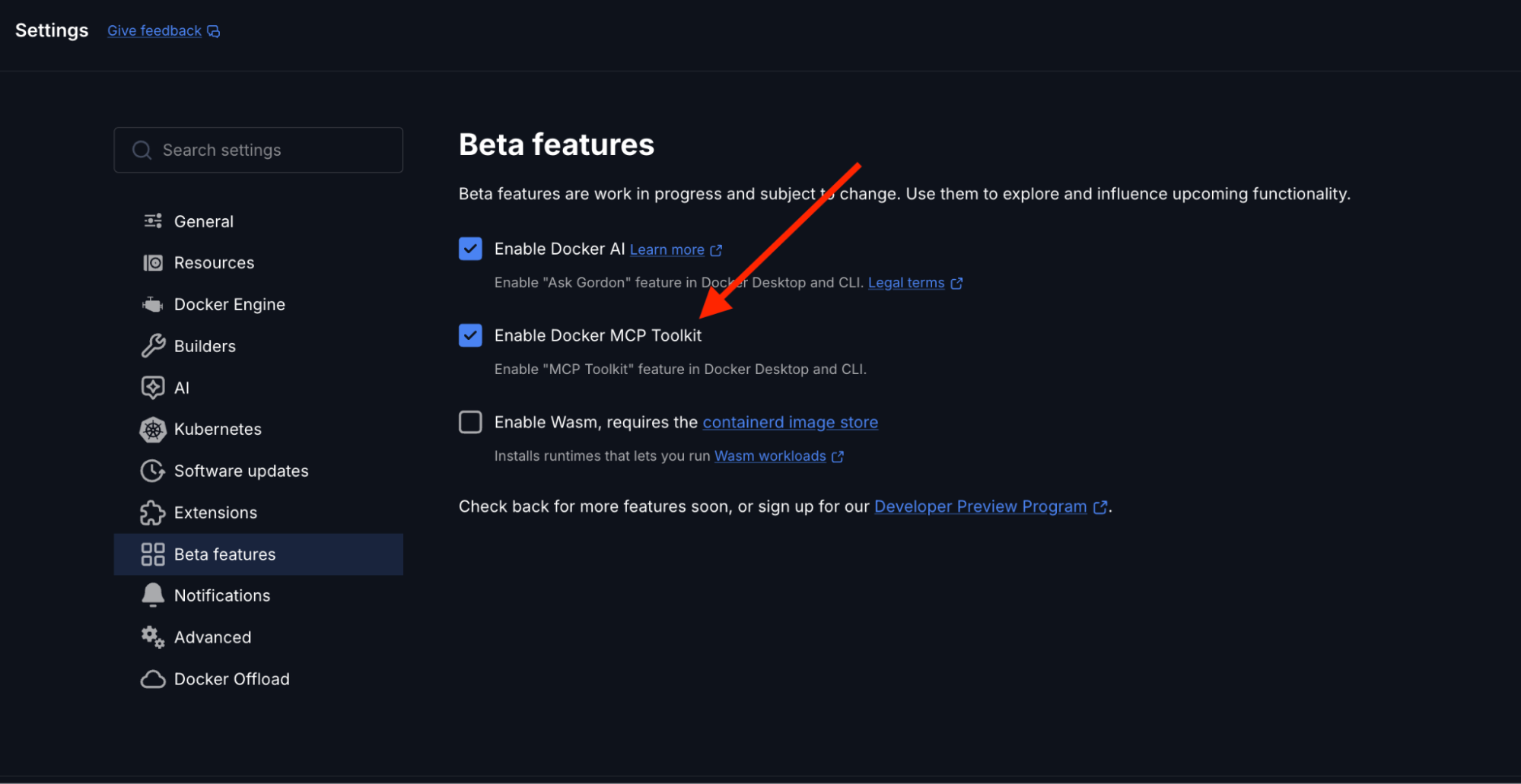
Open Docker Desktop and enable the MCP Toolkit from the Settings menu.
To enable:
- Open Docker Desktop
- Go to Settings → Beta Features
- Toggle Docker MCP Toolkit ON
- Click Apply
Click MCP Toolkit in the Docker Desktop sidebar, then select Catalog to explore available servers.
For this demonstration, we’ll use seven MCP servers:
- SQLite – RDBMS with advanced analytics, text and vector search, geospatial capabilities, and intelligent workflow automation
- Stripe – Updates your product prices to match or beat competitors for automated repricing workflows
- GitHub – Handles version control and deployment
- Firecrawl – Web scraping and content extraction
- Node.js Sandbox – Runs tests, installs dependencies, validates code (in isolated containers)
- Sequential Thinking – Debugs failing tests and optimizes code
- Context7 – Provides code documentation for LLMs and AI code editors
Let’s configure each one step by step.
1. Configure SQLite MCP Server
The SQLite MCP Server requires no external database setup. It manages database creation and queries through its 25 built-in tools.
To setup the SQLite MCP Server, follow these steps:
- Open Docker Desktop → access MCP Toolkit → Catalog
- Search “SQLite”
- Click + Add
- No configuration needed, just click Start MCP Server
docker mcp server ls
# Should show sqlite-mcp-server as enabled
That’s it. ChatGPT can now create databases, tables, and run queries through conversation.
2. Configure Stripe MCP Server
The Stripe MCP server gives ChatGPT full access to payment infrastructure—listing products, managing prices, and updating your catalog to stay competitive.
Get Stripe API Key
- Go to dashboard.stripe.com
- Navigate to Developers → API Keys
- Copy your Secret Key:
- Use
sk_test_... for sandbox/testing
- Use
sk_live_... for production
Configure in Docker Desktop
- Open Docker Desktop → MCP Toolkit → Catalog
- Search for “Stripe”
- Click + Add
- Go to the Configuration tab
- Add your API key:
- Field:
stripe.api_key
- Value: Your Stripe secret key
- Click Save and Start Server
Or via CLI:
docker mcp secret set STRIPE.API_KEY="sk_test_your_key_here"
docker mcp server enable stripe
3. Configure GitHub Official MCP Server
The GitHub MCP server lets ChatGPT create repositories, manage issues, review pull requests, and more.
Option 1: OAuth Authentication (Recommended)
OAuth is the easiest and most secure method:
- In MCP Toolkit → Catalog, search “GitHub Official”
- Click + Add
- Go to the OAuth tab in Docker Desktop
- Find the GitHub entry
- Click “Authorize”
- Your browser opens GitHub’s authorization page
- Click “Authorize Docker” on GitHub
- You’re redirected back to Docker Desktop
- Return to the Catalog tab, find GitHub Official
- Click Start Server
Advantage: No manual token creation. Authorization happens through GitHub’s secure OAuth flow with automatic token refresh.
Option 2: Personal Access Token
If you prefer manual control or need specific scopes:
Step 1: Create GitHub Personal Access Token
- Go to https://github.com and sign in
- Click your profile picture → Settings
- Scroll to “Developer settings” in the left sidebar
- Click “Personal access tokens” → “Tokens (classic)”
- Click “Generate new token” → “Generate new token (classic)”
- Name it: “Docker MCP ChatGPT”
- Select scopes:
repo (Full control of repositories)workflow (Update GitHub Actions workflows)read:org (Read organization data)
- Click “Generate token”
- Copy the token immediately (you won’t see it again!)
Step 2: Configure in Docker Desktop
In MCP Toolkit → Catalog, find GitHub Official:
- Click + Add (if not already added)
- Go to the Configuration tab
- Select “Personal Access Token” as the authentication method
- Paste your token
- Click Start Server
Or via CLI:
docker mcp secret set GITHUB.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN="github_pat_YOUR_TOKEN_HERE"
Verify GitHub Connection
docker mcp server ls
# Should show github as enabled
4. Configure Firecrawl MCP Server
The Firecrawl MCP server gives ChatGPT powerful web scraping and search capabilities.
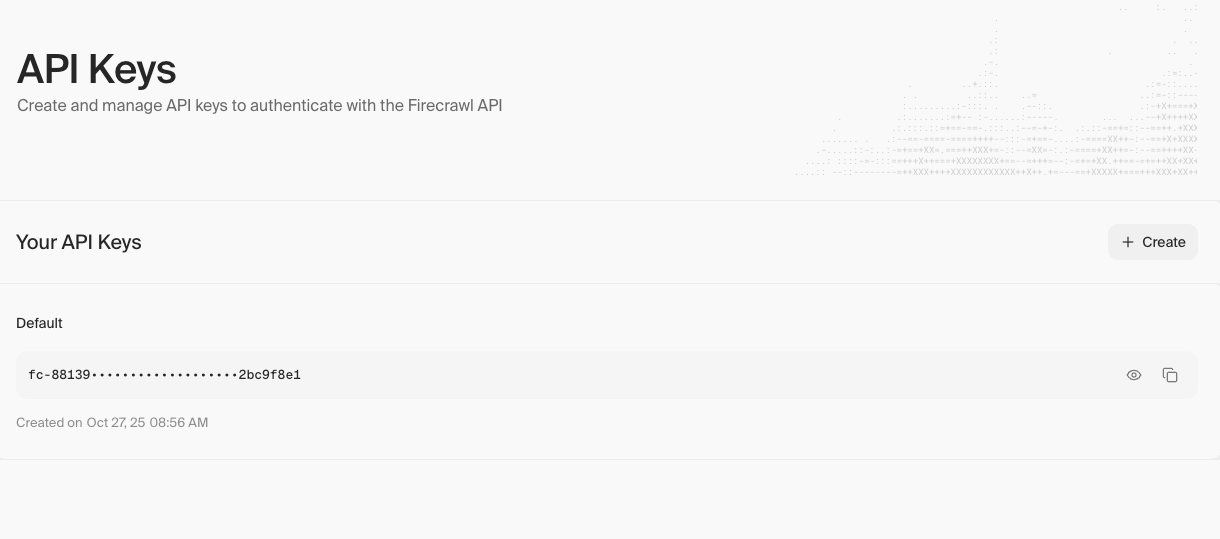
Get Firecrawl API Key
- Go to https://www.firecrawl.dev
- Create an account (or sign in)
- Navigate to API Keys in the sidebar
- Click “Create New API Key”
- Copy the API key
Configure in Docker Desktop
- Open Docker Desktop → MCP Toolkit → Catalog
- Search for “Firecrawl”
- Find Firecrawl in the results
- Click + Add
- Go to the Configuration tab
- Add your API key:
- Field:
firecrawl.api_key
- Value: Your Firecrawl API key
- Leave all other entries blank
- Click Save and Add Server
Or via CLI:
docker mcp secret set FIRECRAWL.API_KEY="fc-your-api-key-here"
docker mcp server enable firecrawl
What You Get
6+ Firecrawl tools, including:
firecrawl_scrape – Scrape content from a single URLfirecrawl_crawl – Crawl entire websites and extract contentfirecrawl_map – Discover all indexed URLs on a sitefirecrawl_search – Search the web and extract contentfirecrawl_extract – Extract structured data using LLM capabilitiesfirecrawl_check_crawl_status – Check crawl job status
5. Configure Node.js Sandbox MCP Server
The Node.js Sandbox enables ChatGPT to execute JavaScript in isolated Docker containers.
Note: This server requires special configuration because it uses Docker-out-of-Docker (DooD) to spawn containers.
Understanding the Architecture
The Node.js Sandbox implements the Docker-out-of-Docker (DooD) pattern by mounting /var/run/docker.sock. This gives the sandbox container access to the Docker daemon, allowing it to spawn ephemeral sibling containers for code execution.
When ChatGPT requests JavaScript execution:
- Sandbox container makes Docker API calls
- Creates temporary Node.js containers (with resource limits)
- Executes code in complete isolation
- Returns results
- Auto-removes the container
Security Note: Docker socket access is a privilege escalation vector (effectively granting root-level host access). This is acceptable for local development but requires careful consideration for production use.
Add Via Docker Desktop
- MCP Toolkit → Catalog
- Search “Node.js Sandbox”
- Click + Add
Unfortunately, the Node.js Sandbox requires manual configuration that can’t be done entirely through the Docker Desktop UI. We’ll need to configure ChatGPT’s connector settings directly.
Prepare Output Directory
Create a directory for sandbox output:
# macOS/Linux
mkdir -p ~/Desktop/sandbox-output
# Windows
mkdir %USERPROFILE%\Desktop\sandbox-output
Configure Docker File Sharing
Ensure this directory is accessible to Docker:
- Docker Desktop → Settings → Resources → File Sharing
- Add
~/Desktop/sandbox-output (or your Windows equivalent)
- Click Apply & Restart
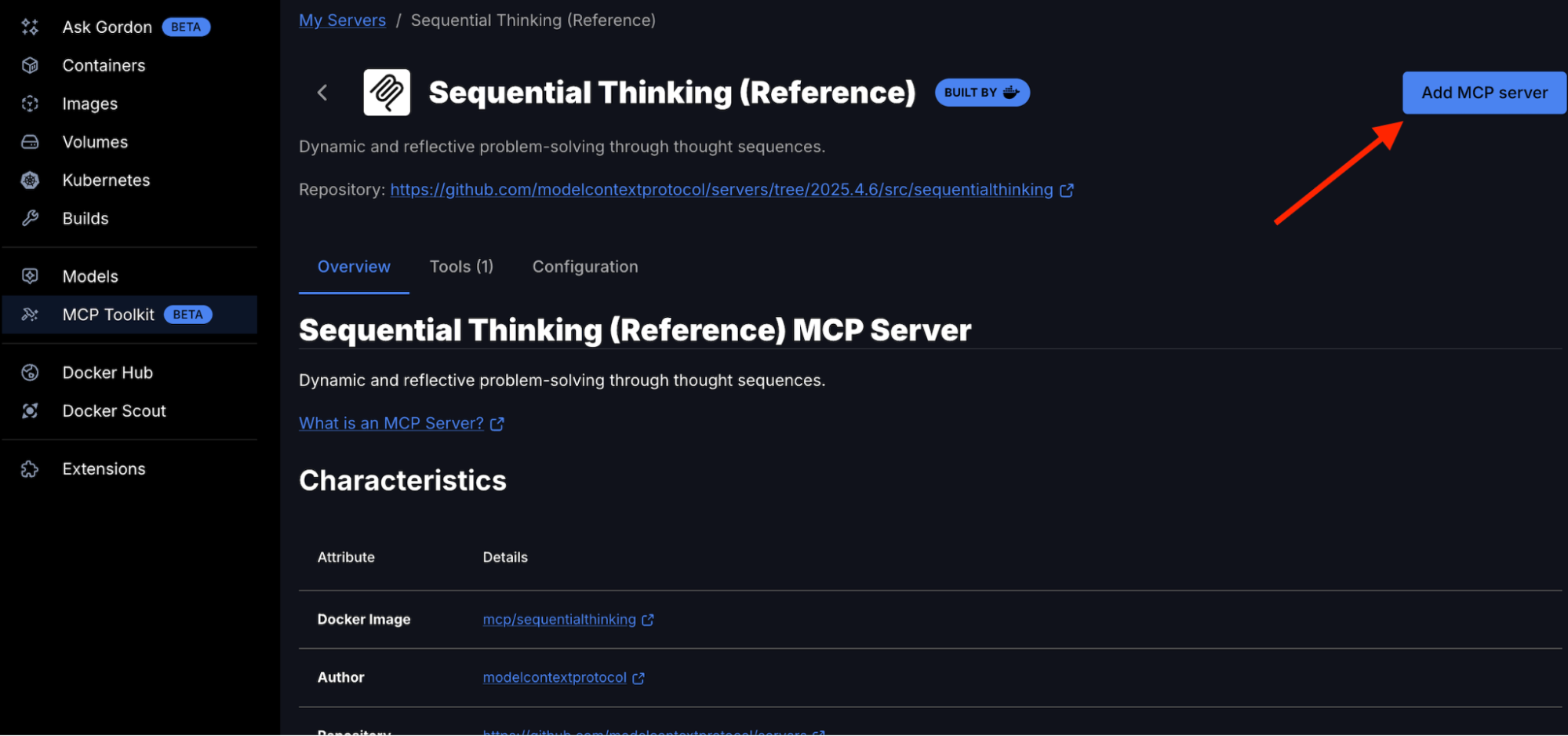
6. Configure Sequential Thinking MCP Server
The Sequential Thinking MCP server gives ChatGPT the ability for dynamic and reflective problem-solving through thought sequences. Adding the Sequential Thinking MCP server is straightforward – it doesn’t require any API key. Just search for Sequential Thinking in the Catalog and get it to your MCP server list.
In Docker Desktop:
- Open Docker Desktop → MCP Toolkit → Catalog
- Search for “Sequential Thinking”
- Find Sequential Thinking in the results
- Click “Add MCP Server” to add without any configuration
The Sequential Thinking MCP server should now appear under “My Servers” in Docker MCP Toolkit.
What you get:
- A single Sequential Thinking tool that includes:
sequentialthinking – A detailed tool for dynamic and reflective problem-solving through thoughts. This tool helps analyze problems through a flexible thinking process that can adapt and evolve. Each thought can build on, question, or revise previous insights as understanding deepens.
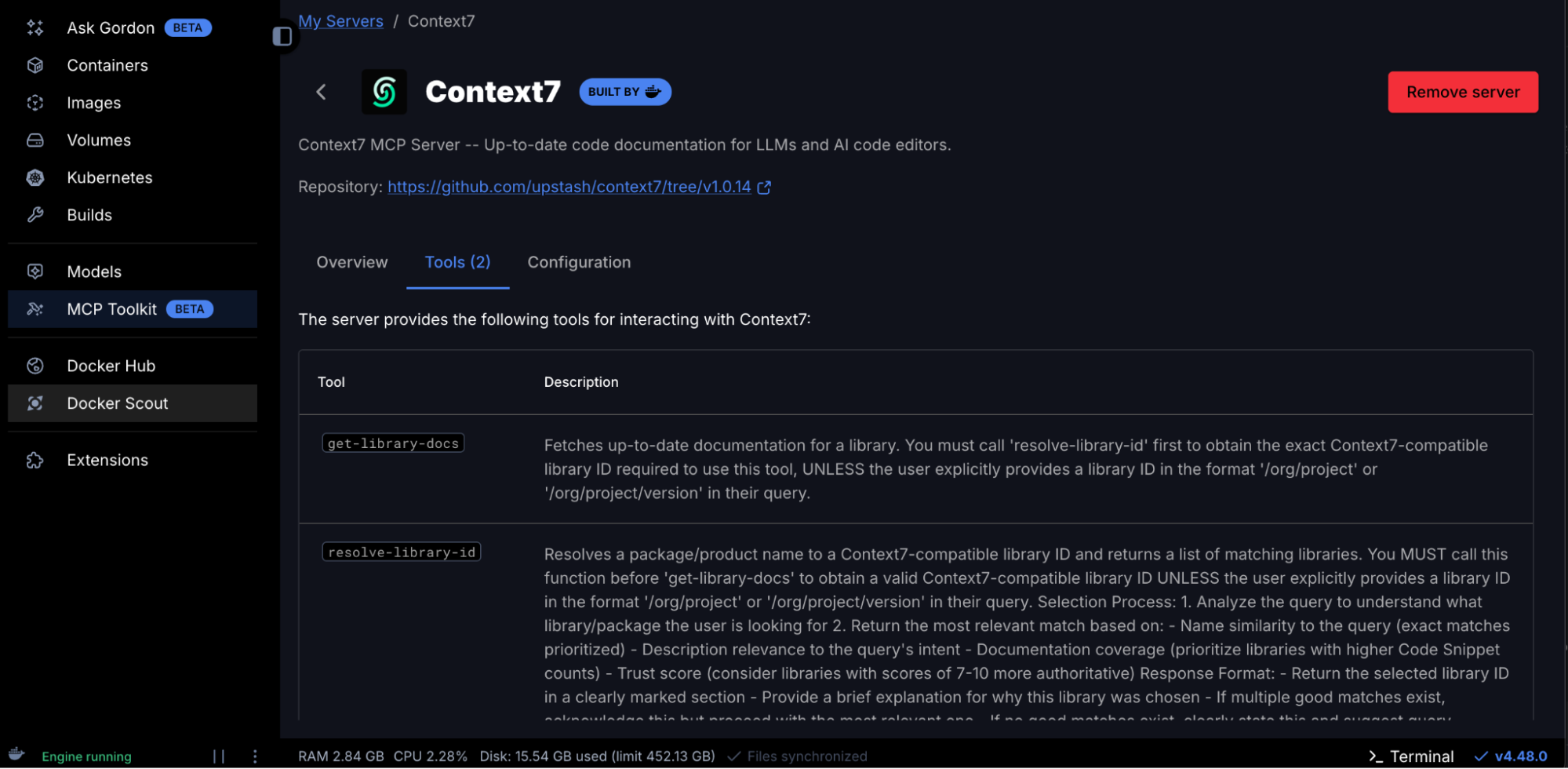
7. Configure Context7 MCP Server
The Context7 MCP enables ChatGPT to access the latest and up-to-date code documentation for LLMs and AI code editors. Adding the Context7 MCP server is straightforward. It doesn’t require any API key. Just search for Context7 in the Catalog and get it added to the MCP server lists.
In Docker Desktop:
- Open Docker Desktop → MCP Toolkit → Catalog
- Search for “Context7”
- Find Context7 in the results
- Click “Add MCP Server” to add without any configuration
The Context7 MCP server should now appear under “My Servers” in Docker MCP Toolkit
What you get:
- 2 Context7 tools including:
get-library-docs – Fetches up-to-date documentation for a library.resolve-library-id – Resolves a package/product name to a Context7-compatible library ID and returns a list of matching libraries.
Verify if all the MCP servers are available and running.
docker mcp server ls
MCP Servers (7 enabled)
NAME OAUTH SECRETS CONFIG DESCRIPTION
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
context7 - - - Context7 MCP Server -- Up-to-da...
fetch - - - Fetches a URL from the internet...
firecrawl - ✓ done partial Official Firecrawl MCP Server...
github-official ✓ done ✓ done - Official GitHub MCP Server, by ...
node-code-sandbox - - - A Node.js–based Model Context P...
sequentialthinking - - - Dynamic and reflective problem-...
sqlite-mcp-server - - - The SQLite MCP Server transform...
stripe - ✓ done - Interact with Stripe services o...
Tip: To use these servers, connect to a client (IE: claude/cursor) with docker mcp client connect <client-name>
Configuring ChatGPT App and Connector
Use the following compose file in order to let ChatGPT discover all the tools under Docker MCP Catalog:
services:
gateway:
image: docker/mcp-gateway
command:
- --catalog=/root/.docker/mcp/catalogs/docker-mcp.yaml
- --servers=context7,firecrawl,github-official,node-code-sandbox,sequentialthinking,sqlite-mcp-server,stripe
- --transport=streaming
- --port=8811
environment:
- DOCKER_MCP_IN_CONTAINER=1
volumes:
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
- ~/.docker/mcp:/root/.docker/mcp:ro
ports:
- "8811:8811"
By now, you should be able to view all the MCP tools under ChatGPT Developer Mode.
Let’s Test it Out
Now we give ChatGPT its intelligence. Copy this system prompt and paste it into your ChatGPT conversation:
You are a Competitive Repricing Agent that monitors competitor prices, automatically adjusts your Stripe product prices, and provides strategic recommendations using 7 MCP servers: Firecrawl (web scraping), SQLite (database), Stripe (price management), GitHub (reports), Node.js Sandbox (calculations), Context7 (documentation), and Sequential Thinking (complex reasoning).
DATABASE SCHEMA
Products table: id (primary key), sku (unique), name, category, brand, stripe_product_id, stripe_price_id, current_price, created_at
Price_history table: id (primary key), product_id, competitor, price, original_price, discount_percent, in_stock, url, scraped_at
Price_alerts table: id (primary key), product_id, competitor, alert_type, old_price, new_price, change_percent, created_at
Repricing_log table: id, product_name, competitor_triggered, competitor_price, old_stripe_price, new_stripe_price, repricing_strategy, stripe_price_id, triggered_at, status
Indexes: idx_price_history_product on (product_id, scraped_at DESC), idx_price_history_competitor on (competitor)
WORKFLOW
On-demand check: Scrape (Firecrawl) → Store (SQLite) → Analyze (Node.js) → Report (GitHub)
Competitive repricing: Scrape (Firecrawl) → Compare to your price → Update (Stripe) → Log (SQLite) → Report (GitHub)
STRIPE REPRICING WORKFLOW
When competitor price drops below your current price:
1. list_products - Find your existing Stripe product
2. list_prices - Get current price for the product
3. create_price - Create new price to match/beat competitor (prices are immutable in Stripe)
4. update_product - Set the new price as default
5. Log the repricing decision to SQLite
Price strategies:
- "match": Set price equal to lowest competitor
- "undercut": Set price 1-2% below lowest competitor
- "margin_floor": Never go below your minimum margin threshold
Use Context7 when: Writing scripts with new libraries, creating visualizations, building custom scrapers, or needing latest API docs
Use Sequential Thinking when: Making complex pricing strategy decisions, planning repricing rules, investigating market anomalies, or creating strategic recommendations requiring deep analysis
EXTRACTION SCHEMAS
Amazon: title, price, list_price, rating, reviews, availability
Walmart: name, current_price, was_price, availability
Best Buy: product_name, sale_price, regular_price, availability
RESPONSE FORMAT
Price Monitoring: Products scraped, competitors covered, your price vs competitors
Repricing Triggers: Which competitor triggered, price difference, strategy applied
Price Updated: New Stripe price ID, old vs new price, margin impact
Audit Trail: GitHub commit SHA, SQLite log entry, timestamp
TOOL ORCHESTRATION PATTERNS
Simple price check: Firecrawl → SQLite → Response
Trend analysis: SQLite → Node.js → Response
Strategy analysis: SQLite → Sequential Thinking → Response
Competitive repricing: Firecrawl → Compare → Stripe → SQLite → GitHub
Custom tool development: Context7 → Node.js → GitHub
Full intelligence report: Firecrawl → SQLite → Node.js → Sequential Thinking → GitHub
KEY USAGE PATTERNS
Use Stripe for: Listing products, listing prices, creating new prices, updating product default prices
Use Sequential Thinking for: Pricing strategy decisions (match, undercut, or hold), market anomaly investigations (why did competitor prices spike), multi-factor repricing recommendations
Use Context7 for: Getting documentation before coding, learning new libraries on-the-fly, ensuring code uses latest API conventions
Use Node.js for: Statistical calculations (moving averages, standard deviation, volatility), chart generation, margin calculations
BEST PRACTICES
Space web scraping requests 2 seconds apart to respect rate limits
Calculate price difference as (your_price - competitor_price)
Trigger repricing when competitor drops below your current price
Log all repricing decisions to SQLite with Stripe IDs for audit trail
Push pricing reports to GitHub for compliance
Always use Context7 before writing code with unfamiliar libraries
Respect margin floors—never reprice below minimum acceptable margin
COMMAND RECOGNITION PATTERNS
"Check X prices and stay competitive" → Full repricing pipeline: scrape → compare → if competitor lower: Stripe update + SQLite + GitHub
"Match competitor price for X" → Stripe: list_products → list_prices → create_price (matching)
"Undercut competitors on X" → Stripe: create_price (1-2% below lowest)
"Show price history" → SQLite query → format results
"Analyze pricing strategy for X" → Sequential Thinking analysis
"Why did competitor prices change" → Query data → Sequential Thinking investigation
CORE PRINCIPLE
When competitors change prices, don't just report—ACT. Update your Stripe prices to stay competitive, log decisions to SQLite, push audit records to GitHub. Transform competitor intelligence into automated repricing. All data stays on YOUR infrastructure.
Here’s the prompt:
Set up a competitive repricing agent:
1. I sell MacBook Air M3 on my store - current Stripe price is $549.99
2. Monitor competitor prices on Amazon, Walmart, Best Buy
3. When ANY competitor drops below my price:
- Automatically update my Stripe product price to match or beat them
- Use "undercut" strategy (price 1% below lowest competitor)
- Log the repricing decision to SQLite
- Push pricing change report to GitHub
Check prices now and reprice if needed.
Here’s how ChatGPT responds – orchestrating all 7 MCP servers in a single workflow:
Competitive Repricing Agent – Execution Complete
Within 3 minutes, ChatGPT orchestrated all 7 MCP servers to analyse the market and automatically reprice your product.
Repricing Triggered and Executed:
|
Your Price
|
$549.99
|
$504.99
|
|
Price Change
|
–
|
-$45.00 (-8.2%)
|
|
Market Position
|
3rd (behind Best Buy)
|
#1 Lowest
|
Competitor Price Scan Results:
|
Your Store
|
$504.99
|
Market Leader
|
|
Best Buy
|
$509.99
|
+$5.00 (you beat by 1%)
|
|
Walmart
|
$669.00
|
+$164.01 higher
|
|
Amazon
|
$699.00
|
+$194.01 higher
|
What the Agent did (6 Steps):
- Installed SQLite3 and created database schema with 4 tables
- Created Stripe product (prod_TZaK0ARRJ5OJJ8) with initial $549.99 price
- Scraped live competitor prices via Firecrawl from Amazon, Best Buy, and Walmart
- Analysed pricing strategy with Sequential Thinking — detected Best Buy at $509.99 below your price
- Executed repricing — created new Stripe price at $504.99 (price_1ScRCVI9l1vmUkzn0hTnrLmW)
- Pushed audit report to GitHub (commit `64a488aa`)
All data stored on your infrastructure – not OpenAI’s servers.
To check prices again, simply ask ChatGPT to ‘check MacBook Air M3 competitor prices’—it will scrape, compare, and reprice automatically. Run this check daily, weekly, or whenever you want competitive intelligence
Explore the Full Demo
View the complete repricing report and audit trail on GitHub: https://github.com/ajeetraina/competitive-repricing-agent-mcp
Want true automation? This demo shows on-demand repricing triggered by conversation. For fully automated periodic checks, you could build a simple scheduler that calls the OpenAI API every few hours to trigger the same workflow—turning this into a hands-free competitive intelligence system.Default houston Paragraph Text
Wrapping Up
You’ve just connected ChatGPT to Docker MCP Toolkit and configured multiple MCP servers. What used to require context-switching between multiple tools, manual query writing, and hours of debugging now happens through natural conversation, safely executed in Docker containers.
This is the new paradigm for AI-assisted development. ChatGPT isn’t just answering questions anymore. It’s querying your databases, managing your repositories, scraping data, and executing code—all while Docker ensures everything stays secure and contained.
Ready to try it? Open Docker Desktop and explore the MCP Catalog. Start with SQLite, add GitHub, experiment with Firecrawl. Each server unlocks new capabilities.
The future of development isn’t writing every line of code yourself. It’s having an AI partner that can execute tasks across your entire stack securely, reproducibly, and at the speed of thought.
Learn More
from Docker https://ift.tt/Y7dmMhr
via
IFTTT