Hyper-V is a proprietary hypervisor developed by Microsoft. Even though it is used mostly with Windows systems, Hyper-V can run various types of guests, including Windows, Linux, and other Unix-like operating systems. Hyper-V’s integration with other Microsoft products, ease of use and enterprise-level features make it a popular choice for businesses that use Microsoft products and require a robust virtualization solution.
Unlike Hyper-V, KVM is a free and open-source hypervisor that benefits from a large community of developers who contribute to its growth. The fact that KVM is free and its flexibility make it a popular choice for organizations that require a customizable and cost-effective virtualization solution.
Hyper-V vs KVM
Despite having a lot of similarities, Hyper-V and KVM are obviously different in quite a few ways – such as:
- Features: Both hypervisors offer similar virtualization features such as virtual CPU, memory, disk, and network interfaces, but Hyper-V offers more advanced features such as live migration, network virtualization, and support for virtual Fibre Channel.
- Hypervisor: Hyper-V is a hypervisor that runs directly on the host machine’s hardware, while KVM uses the Linux kernel’s virtualization capabilities.
- OS: Hyper-V is a hypervisor primarily designed to run on Windows-based systems, while KVM is included in the Linux kernel and is primarily used on Linux-based systems.
- Cost: Hyper-V requires licensing fees, while KVM is a free and open-source hypervisor.
Convert Hyper-V to KVM using StarWind V2V Converter
Hyper-V and KVM are both popular hypervisors with similar virtualization capabilities. Nevertheless, KVM is open source and self-supported, while Hyper-V, like any proprietary product, requires licensing. It’s no surprise that admins sometimes need an easy way to migrate VMs from one platform to another, depending on current needs and goals.
To do so, there is no better way than to use a converter that works with both Hyper-V and KVM VM formats, such as StarWind V2V Converter / P2V Migrator. It is a specialized solution that provides fast and efficient conversion of virtual machines, minimizing downtime and ensuring that virtual machines are up and running as quickly as possible. StarWind V2V Converter also supports a wide range of virtual machine formats, including VMDK (VMware), VHD (Hyper-V), VHDX (Hyper-V), QCOW2 (KVM), RAW (different solutions), IMG (different solutions), VDI (Oracle VirtualBox), and StarWind native IMG.
It’s time to begin with the conversion process!
The goal is to convert the VM to a standalone KVM host.
1. Select the location of the VM’s disk that needs to be converted.
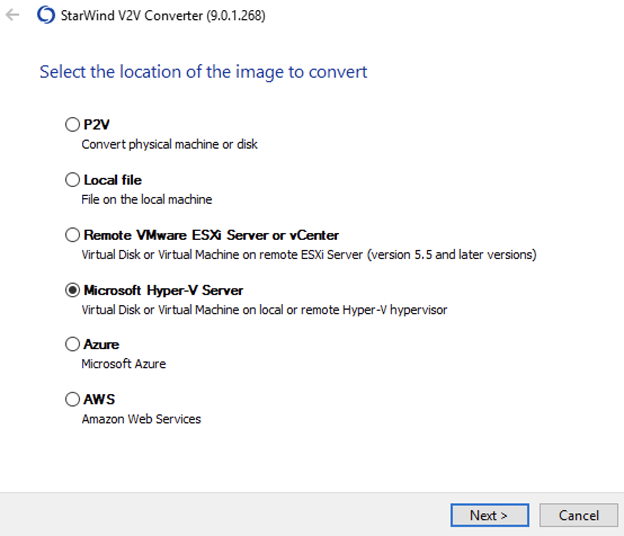
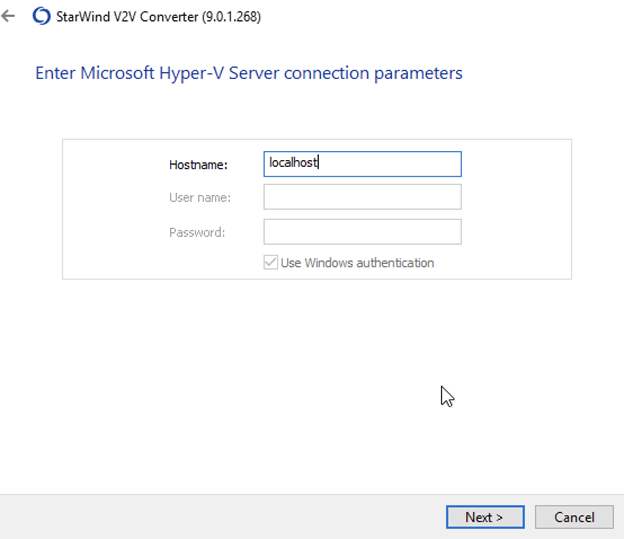
2. Specify IP address, username and password of the Hyper-V host, click Next:
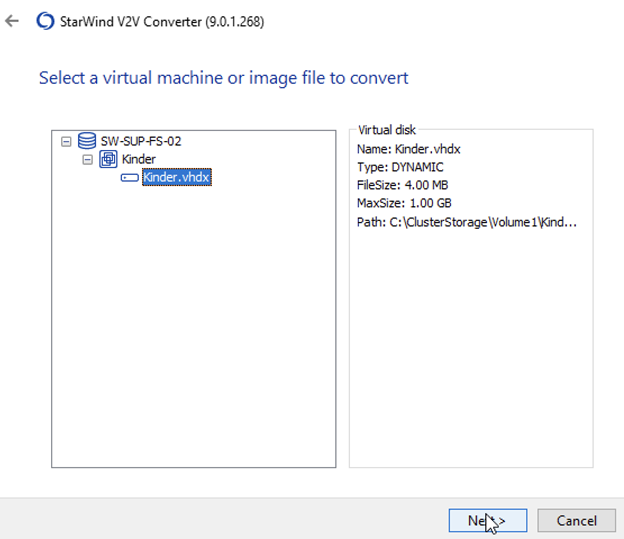
3. Select the .vhdx file click Next.
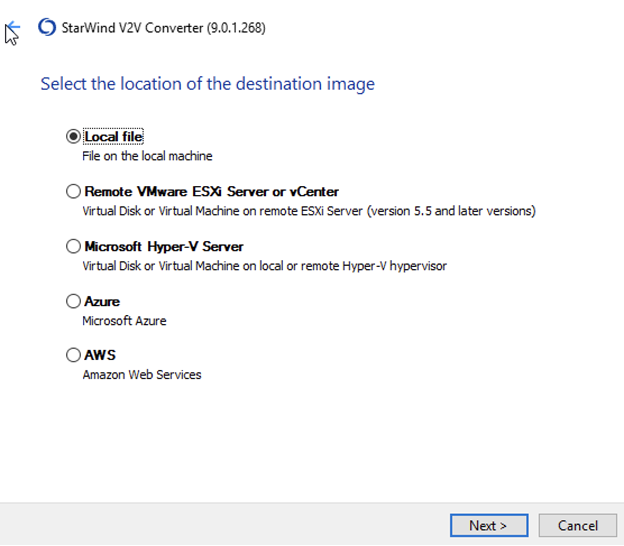
4. Save the destination image as a Local file, click Next.
5. Select QCOW2 as a destination image format, click Next.
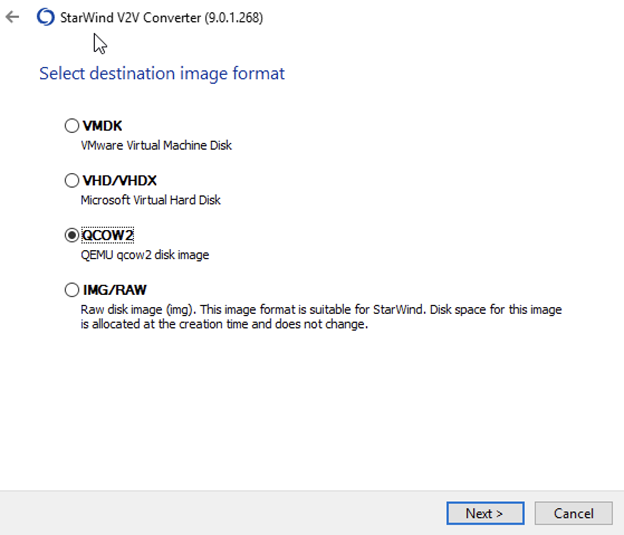
6. Set destination file name, click Convert.
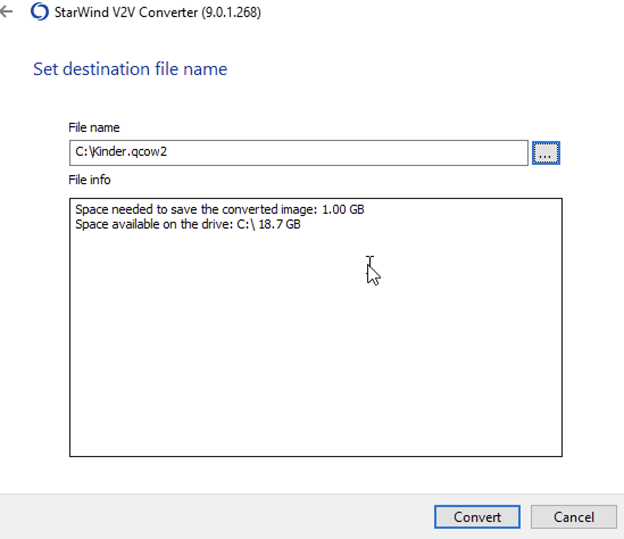
7. The conversion process has begun now. When the conversion process ends, click Finish.
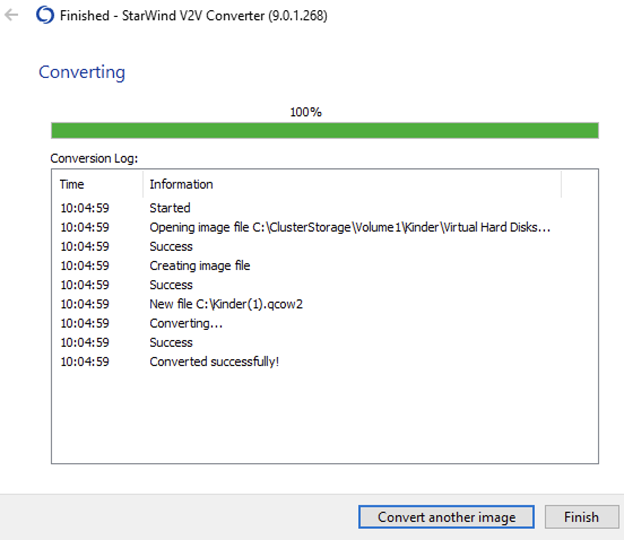
8. The converted .qcow2 disk will be placed locally on the Hyper-V server. Copy the .qcow2 image to the KVM instance using the WinSCP (or similar tools).
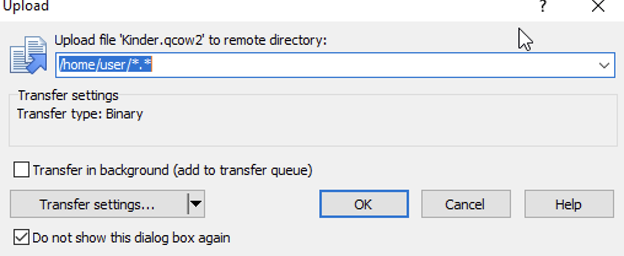
9. Select Virtual machines tab on the KVM server, click Import VM.
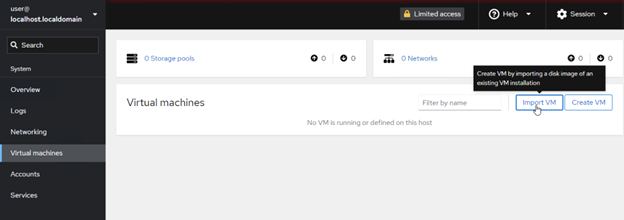
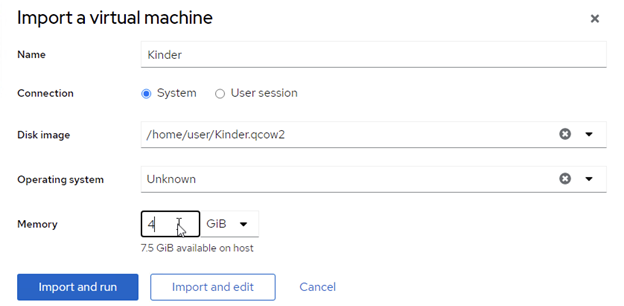
10. Specify the setting for the imported VM (path to the converted disk, select the OS, and assign RAM)
11. Everything is read now. You can run the VM!
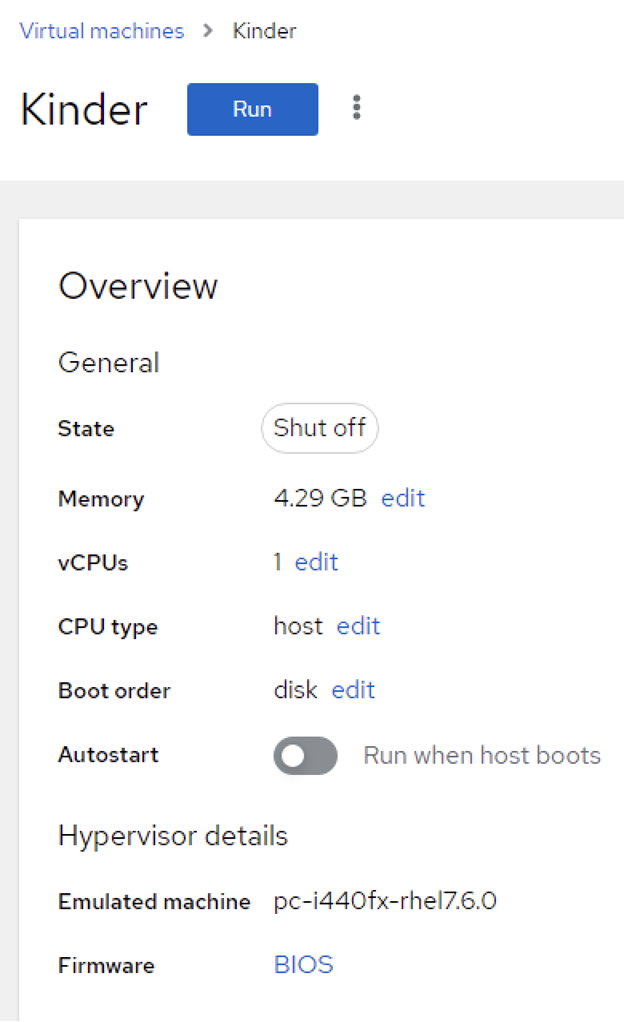
Congratulations, all done!
Conсlusion
While similar, KVM and Hyper-V are different too. For example, KVM uses a para-virtualization technique, which means you need to modify the guest OS. On the other hand, Hyper-V uses full virtualization that requires no such thing. KVM may have better performance and scalability in certain scenarios, but Hyper-V still has better integration with Windows systems and supports advanced features (migration and high availability) almost out of the box. Essentially, the choice depends entirely on you and your specific needs.
This material has been prepared in collaboration with Viktor Kushnir, Technical Writer with almost 4 years of experience at StarWind.
Related materials:
- StarWind V2V Converter: Now with Physical to Virtual (P2V) conversion option!
- How to Convert Hyper-V to VMware VM
- How to convert VMware VM to KVM
from StarWind Blog https://bit.ly/3BbUeU5
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment